PPT Chapters 3133— PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID273579
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, 347 U.S. 483 (1954) Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka. Argued December 9, 1952. Reargued December 8, 1953. Decided May 17, 1954*. Syllabus. Segregation of white and Negro children in the public schools of a State solely on the basis of race, pursuant to state laws permitting or requiring such.. Ferguson case. On May 17, 1954, U.S. Supreme Court Justice Earl Warren delivered the unanimous ruling in the landmark civil rights case Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, Kansas. State-sanctioned segregation of public schools was a violation of the 14th amendment and was therefore unconstitutional. This historic decision marked the end of.

As The 65th Anniversary of Brown v. Board Of Education Passes

83 Background To Brown V Board Of Education Images & Pictures MyWeb

When Did Brown v Board of Education Happen? Education Resource Center

83 Background To Brown V Board Of Education Images & Pictures MyWeb

Plessy V Ferguson Significance / Section 6 Timeline of Significant

How did brown v board of education impact society osedivine

98+ Background Of Brown V. Board Images MyWeb

Brown v. Board of Education by Margeaux Weston Goodreads

83 Background To Brown V Board Of Education Images & Pictures MyWeb

Brown v. Board of Education Historical Marker

PPT Famous Court Cases II PowerPoint Presentation ID4557212

Brown V Board Of Education 1954 Definition DEFINITION FGD

83 Background To Brown V Board Of Education Images & Pictures MyWeb
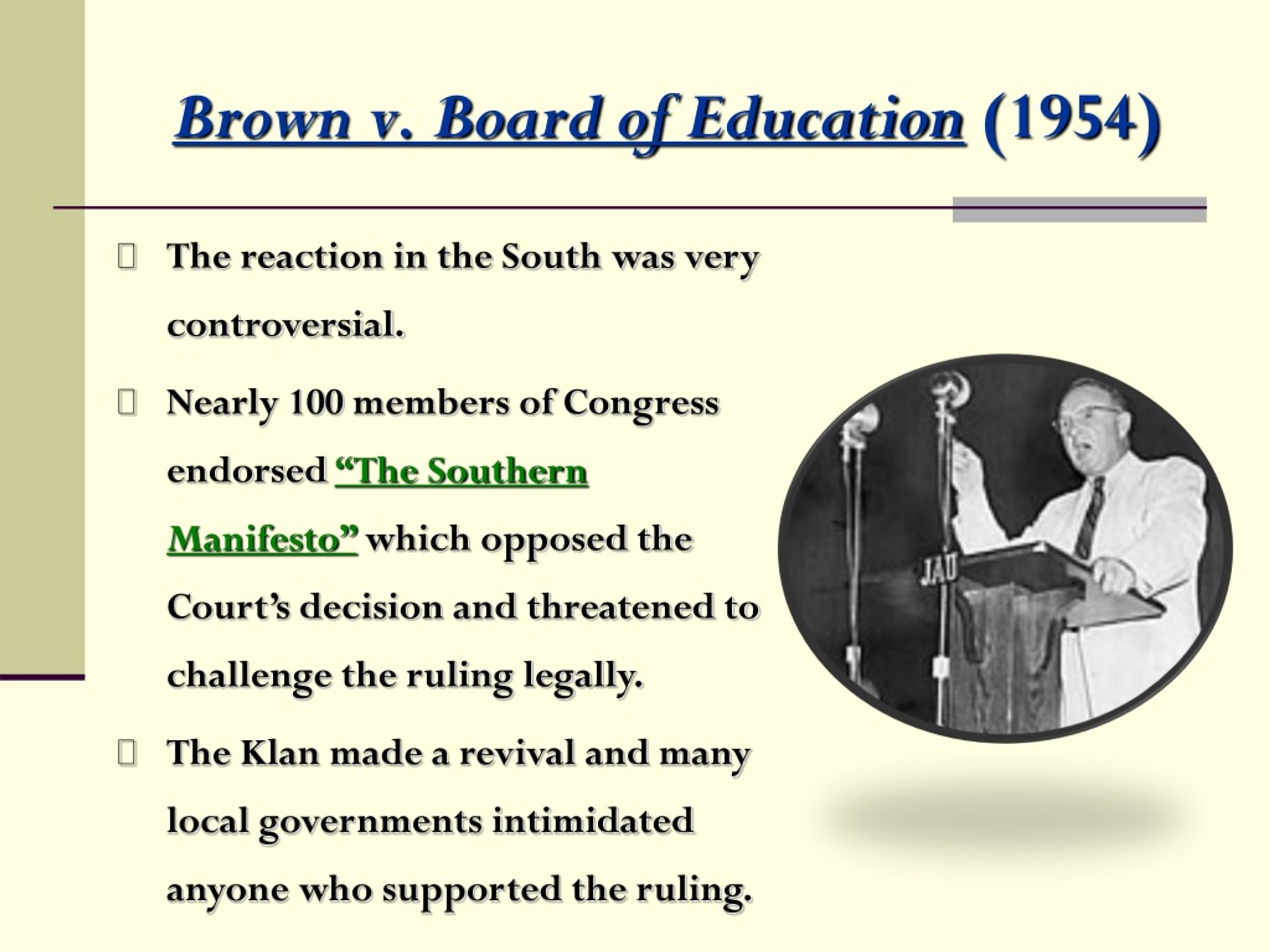
PPT Chapters 3133— PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID273579

Brown v. Board of Education Case Brief Summary Law Case Explained

35 Best Ideas Brown Vs Board Of Education Quotes Home, Family, Style
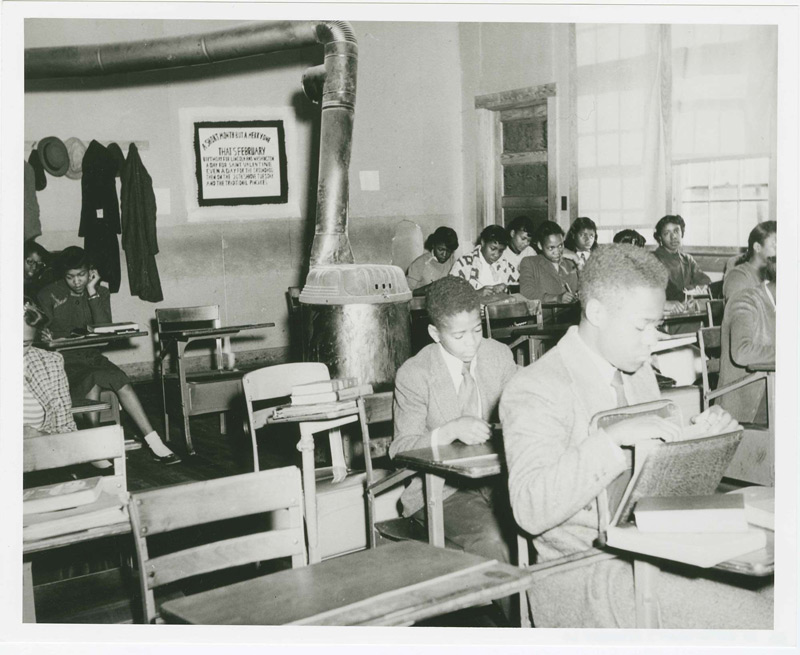

Brown v. Board of Education (2023)
Brown v. Board of Education’s 60th Anniversary Stirs History, Reality
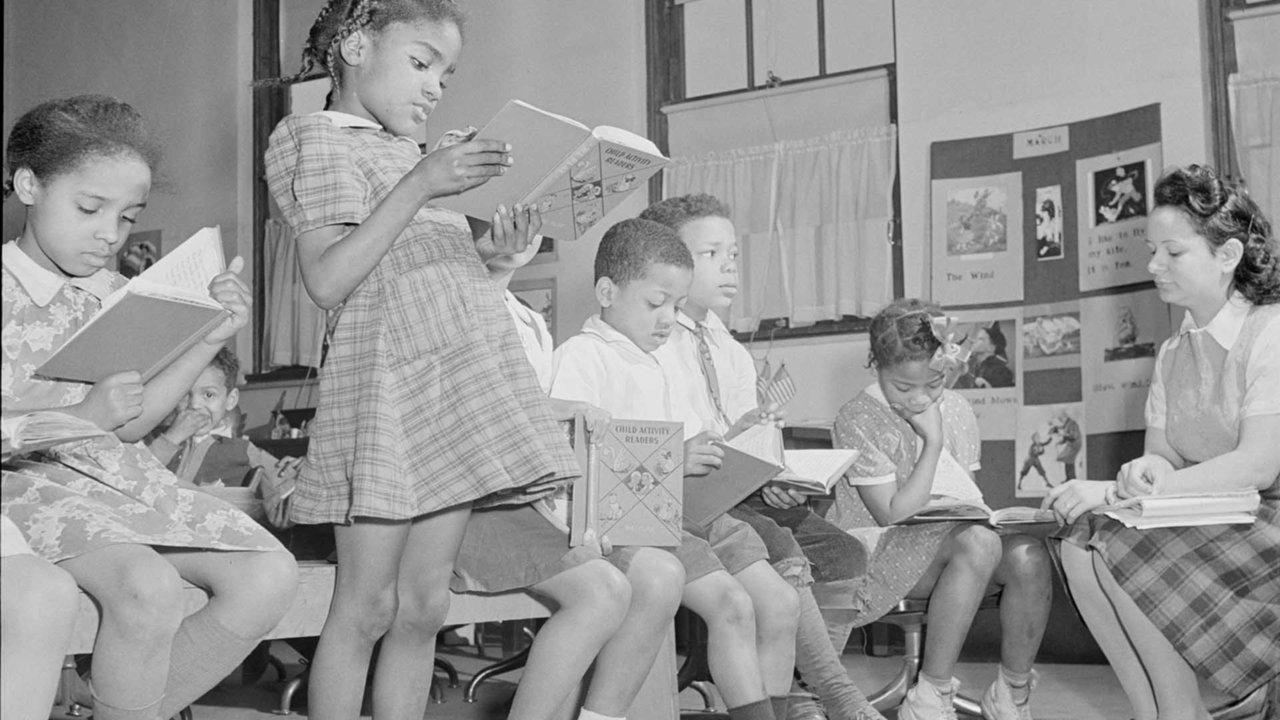

Brown v. Board of Education May 17
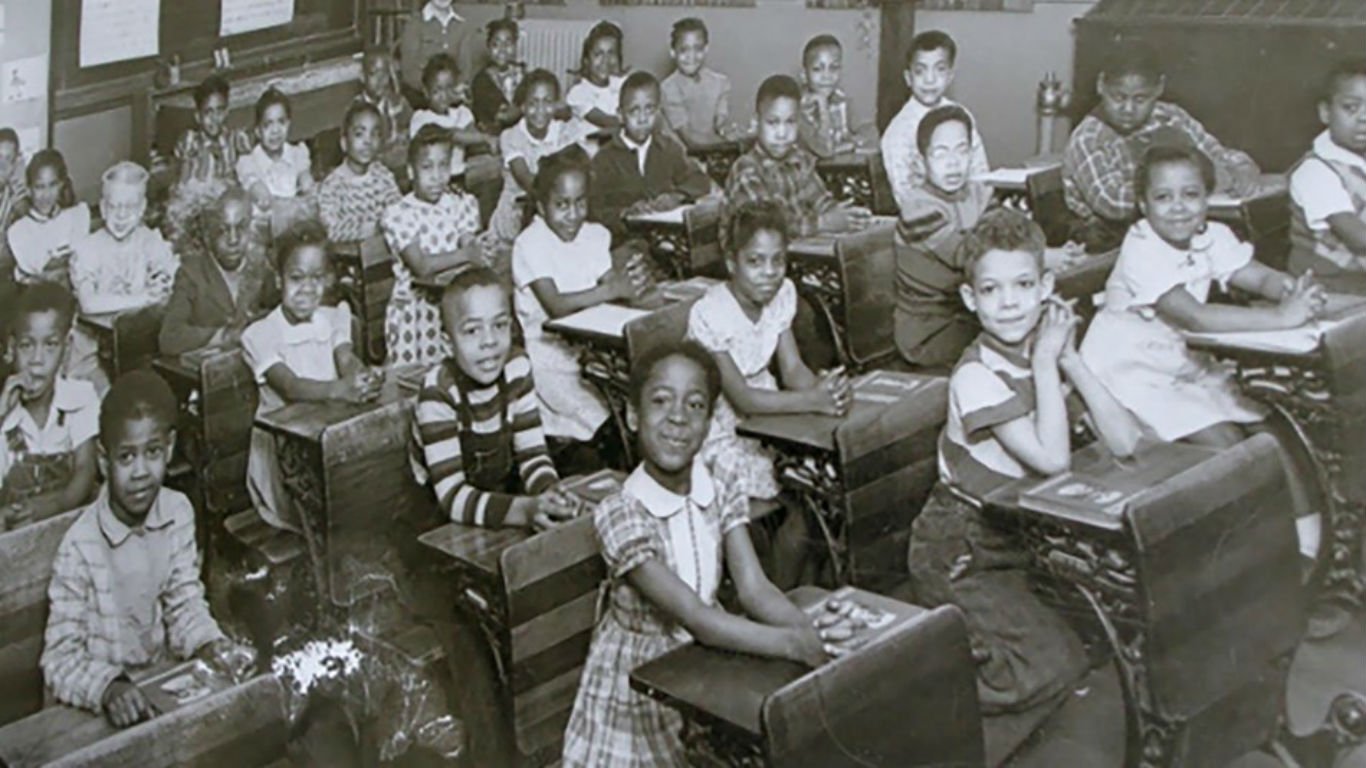

Most Important Event in Every State’s History Page 5 24/7 Wall St.
Kentucky (1908) Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, 347 U.S. 483 (1954), [1] was a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court ruling that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the segregated schools are otherwise equal in quality. The decision partially overruled the Court’s 1896.. Board of Education case was brought, with their parents (L-R) Zelma Henderson, Oliver Brown, Sadie Emanuel, Lucinda Todd, and Lena Carper, 1953. In its landmark ruling, the Supreme Court didn’t.